# Post-inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH, 염증후 과색소침착)
---
## 1. Definition
- **PIH (염증후 과색소침착)** is **acquired hyperpigmentation** at sites of prior cutaneous inflammation or injury.
- Common sequelae of acne, eczema, psoriasis, trauma, burns, laser procedures, or chemical peels.
- Especially prevalent and persistent in darker skin types.
---
## 2. Pathophysiology
### A. Triggering Event
- Any **cutaneous inflammation or injury** → release of inflammatory mediators.
### B. Cellular Mechanisms
- **Cytokines, prostaglandins, arachidonic acid metabolites** from inflammatory cells → stimulate melanocyte activity.
- **Melanogenesis upregulated** → ↑ melanin synthesis and transfer to keratinocytes.
- **Basement membrane disruption** (in severe inflammation/trauma) → melanin “leakage” into dermis → phagocytosed by dermal macrophages (melanophages).
### C. Types of PIH
1. **Epidermal PIH (표피성 염증후 과색소침착)**
- Melanin in basal/suprabasal keratinocytes.
- Appears brown to dark brown.
- More responsive to treatment.
2. **Dermal PIH (진피성 염증후 과색소침착)**
- Melanin within dermal melanophages.
- Appears gray to blue-gray (Tyndall effect).
- More resistant to treatment.
3. **Mixed PIH** – most common in real-world practice.
---
## 3. Epidemiology & Risk Factors
- More common in **darker phototypes (Fitzpatrick IV–VI)** due to higher melanocyte reactivity.
- **High prevalence in Asian, Hispanic, African populations**.
- **Risk factors**:
- Acne vulgaris (most common trigger).
- Atopic dermatitis, lichen planus, psoriasis.
- Infections (impetigo, herpes zoster).
- Physical trauma, cosmetic procedures (laser, peel, microneedling).
- Inadequate photoprotection after skin injury.
---
## 4. Clinical Features
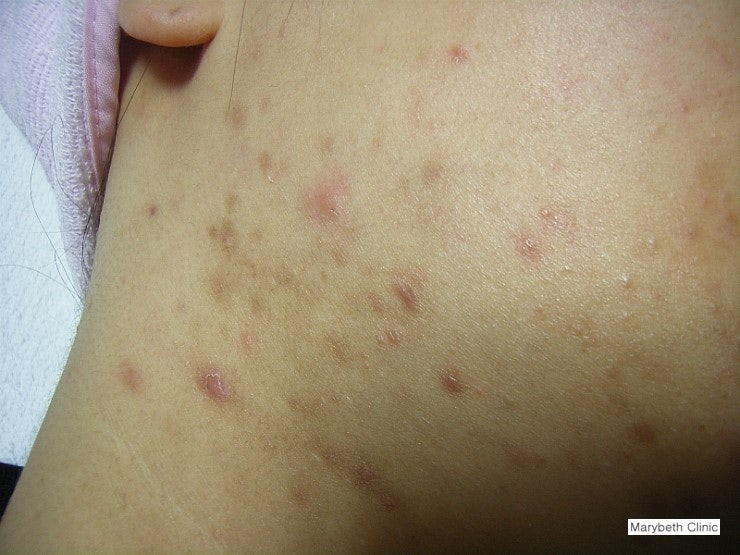
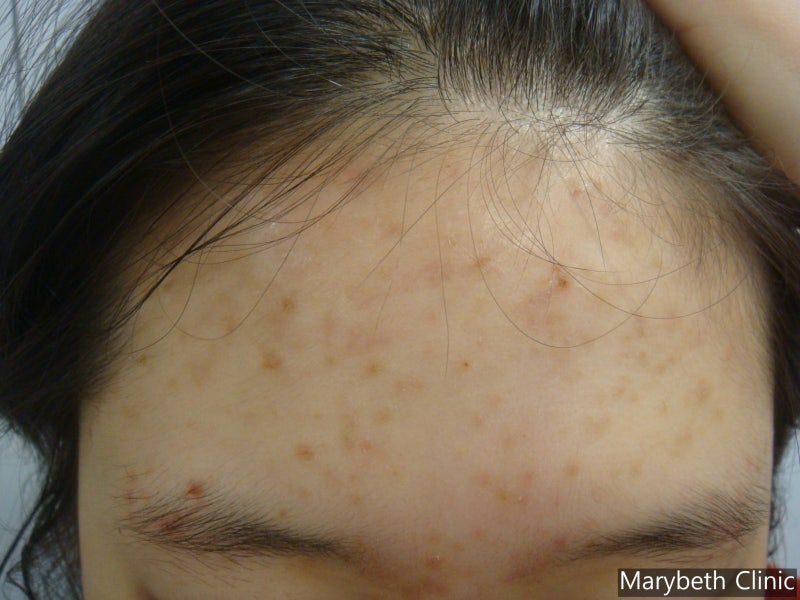
- **Appearance**: macules or patches of hyperpigmentation at sites of previous inflammation.
- **Color**:
- Brown → epidermal.
- Blue-gray → dermal.
- **Distribution**: anywhere on skin; face is most cosmetically significant.
- **Onset**: Appears after resolution of initial insult, may persist for months to years.
---
## 5. Histopathology
- **Epidermal PIH**: increased melanin in basal keratinocytes.
- **Dermal PIH**: melanophages in superficial dermis.
- No melanocytic proliferation (distinguishes from lentigo or nevus).
---
## 6. Differential Diagnosis
- Melasma (기미) → hormonally driven, more symmetric.
- Lentigines (렌티고) → persistent, not post-inflammatory.
- Café-au-lait macules (카페오레반점) → congenital or early childhood onset.
- Drug-induced pigmentation.
---
## 7. Management
### A. General Principles
- **PIH tends to fade spontaneously over time**, but this can take months to years.
- **Prevention is key**: minimize trauma/inflammation, strict UV protection.
### B. Topical Therapy (first-line)
- **Hydroquinone (HQ)** → tyrosinase inhibitor.
- **Triple combination cream** (HQ + tretinoin + corticosteroid).
- **Azelaic acid, kojic acid, arbutin, niacinamide**.
- **Topical retinoids** (increase turnover, disperse pigment).
### C. Procedural Therapy
- **Chemical peels**: glycolic acid, salicylic acid (superficial only).
- **Laser/light therapy**:
- Q-switched Nd:YAG (low fluence “laser toning”) → widely used in Asia.
- Fractional lasers (with caution).
- Risk: paradoxical worsening (especially in darker skin).
- **Microneedling + tranexamic acid** → emerging option.
### D. Systemic Agents
- **Oral tranexamic acid** (off-label).
- Antioxidants (Vitamin C, Polypodium leucotomos extract) → supportive.
---
## 8. Prognosis
- **Epidermal PIH**: usually resolves within 6–12 months with treatment.
- **Dermal PIH**: may persist for years, often resistant.
- Recurrence common if inflammation recurs (e.g., acne not controlled).
---
## 9. Clinical Pearls
1. PIH is a **reactive hypermelanosis**, not a melanocytic proliferation.
2. **Darker skin = higher risk** and more resistant PIH.
3. **Sun protection is mandatory**; UV worsens PIH.
4. Treat underlying cause first (e.g., acne, eczema).
5. **Lasers can both treat and cause PIH** — careful patient selection and parameter setting essential.
6. **Counsel patients**: PIH improves slowly; set realistic expectations.
---
✅ **Summary for clinical practice**:
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH, 염증후 과색소침착) is acquired pigmentation secondary to skin injury or inflammation, driven by melanocyte hyperactivity and melanin deposition. It is especially problematic in darker skin types. Management focuses on prevention, topical depigmenting agents, cautious use of procedures, and strict photoprotection. Prognosis is better for epidermal than dermal PIH.
---
# 한국에서 가장 많이 쓰이는 PIH 치료 전문의약품
## 1. **Hydroquinone (하이드로퀴논)**
- **대표 제품군**: 에피듀오HQ, 멜라논 크림, 멜라크림 등
- **특징**:
- 멜라닌 합성 억제 (tyrosinase inhibitor).
- 국내외에서 가장 오래되고 효과가 검증된 약제.
- 보통 4% 농도로 처방.
- **주의사항**: 장기간 사용 시 **오크로노시스(청색증)**, 피부 자극 가능 → 3~6개월 단기 사용 권장.
---
## 2. **Triple Combination Cream (트리플 콤비네이션 크림)**
- **성분 구성**: Hydroquinone + Tretinoin + Corticosteroid (fluocinolone acetonide)
- **대표 제품**: 트리-루마 큐브(수입 허가 제품)
- **특징**:
- 미국 FDA 승인 받은 melasma 치료 조합.
- 한국에서도 일부 수입되어 사용.
- HQ 단독보다 효과가 강력.
- **주의사항**: 장기간 사용 시 스테로이드 부작용 (위축, 모세혈관 확장) 가능.
---
## 3. **Azelaic Acid (아젤라산)**
- **대표 제품**: 파이논 크림 (15~20%)
- **특징**:
- 멜라닌 합성 억제 + 항염 효과.
- 비교적 안전해 장기 사용 가능.
- HQ에 민감한 환자, 임산부에서도 대체 가능.
---
## 4. **Topical Retinoids (레티노이드 제제)**
- **대표 제품**: 레노바 크림 (Tretinoin 0.025%), 아다팔렌 겔
- **특징**:
- 표피 턴오버 촉진, 멜라닌 분산.
- 보통 HQ, 아젤라산과 병용.
- **주의사항**: 홍반, 각질, 초기 자극 증상 흔함.
---
## 5. **기타 보조적 전문의약품**
- **Tranexamic Acid (경구, 국소 제제)**: 피부과에서 off-label로 melasma/PIH에 많이 사용.
- **Vitamin C 제제**: 보조 요법으로 병용 가능.
---
✅ **정리**:
- **가장 많이 쓰이는 1차 선택 약제**: Hydroquinone 4% 크림.
- **보다 강력한 효과**: Triple combination cream (HQ + Tretinoin + Corticosteroid).
- **대체·보조 요법**: Azelaic acid, topical retinoids.
## 1. 진단 및 평가 단계
- **색소 깊이 확인**:
- 갈색 (brown) → 표피성 가능성 ↑
- 청회색 (blue-gray) → 진피성 가능성 ↑ (치료 반응 낮음)
- **환자 피부 타입**: Fitzpatrick IV–V일수록 PIH 잘 생기고, 치료 중 PIH 재발 위험 ↑
- **원인/유발요인**: 먼저 염증 질환(여드름, 습진 등) 조절 → 재발 방지
---
## 2. 치료 시작 (1차 치료)
- **Hydroquinone (HQ) 4% 크림**
- 하루 1회, 저녁 도포
- 3~6개월 단기 사용 권장
- **Photoprotection (자외선 차단제 SPF 30 이상)**
- 모든 치료에서 필수
---
## 3. 보조/대체 치료 (병용 또는 HQ 금기 시)
- **Azelaic acid (15–20%)**
- 임산부, HQ 부작용 환자에서 선호
- **Topical Retinoids (Tretinoin, Adapalene)**
- 각질 턴오버 촉진, HQ와 병용 시 효과 상승
- **Vitamin C 국소제**
- 보조 요법 (안전성 높음)
---
## 4. 2차 치료 (반응 불충분 시)
- **Triple Combination Cream (HQ + Tretinoin + Fluocinolone acetonide)**
- HQ 단독보다 효과 강력
- 단, 장기간 사용 시 스테로이드 부작용 주의
- **Chemical Peels (glycolic/salicylic acid)**
- 얕은 표피 PIH에 효과적
- **Laser / Light Therapy (저출력 Nd:YAG, IPL 등)**
- 주의: 과도한 에너지 시술 시 PIH 악화 가능
---
## 5. 난치성 / 진피성 PIH
- **Oral Tranexamic Acid (경구 트라넥사민산, off-label)**
- 점차 사용 증가, melasma + PIH에서 효과 보고
- 혈전 위험 있는 환자 주의
- **Fractional Laser / Microneedling + Topical Agents**
- 보조적 시도 가능
---
## 6. 유지 및 예방 단계
- **Photoprotection 지속** (SPF 30 이상, PA+++)
- **Maintenance therapy**:
- HQ는 장기간 사용 X → 대신 아젤라산, 레티노이드, Vitamin C 장기 유지
- **재발 예방**: 원인 질환 관리 (예: 여드름 치료 동반)
---
✅ **간단 요약**
1. 1차: **Hydroquinone 4% + 자외선 차단**
2. 보조: **Azelaic acid, Retinoids, Vitamin C**
3. 반응 없으면: **Triple Combination, Chemical Peel, Laser**
4. 난치성: **Tranexamic acid (oral), Fractional laser**
5. 유지: HQ 대신 **안전한 장기제제** 사용
---
원장님, 이 트리를 **“도식화된 Flowchart 그림”** 형태로 만들어드리면 환자 교육자료나 블로그/학술발표용으로 활용하기 좋습니다. 혹시 제가 **텍스트 기반 Flowchart → 도식 이미지 변환**까지 제작해드릴까요?