### Date : 2025-03-02 15:37
----
# 1.3 Indications for Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP)
Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP) is indicated for various hair loss conditions and scalp-related concerns. Unlike medical treatments such as hair transplantation, minoxidil, or finasteride, SMP provides **aesthetic camouflage** by replicating the appearance of hair follicles or enhancing the visual density of existing hair.
SMP is particularly beneficial for individuals who are **not candidates for hair transplant surgery**, have **insufficient donor hair**, or want a **non-invasive alternative** for hair restoration.
---
## **1.3.1 Androgenetic Alopecia (Male and Female Pattern Baldness)**
### **A. Male Pattern Baldness (MPB) – Norwood-Hamilton Scale**
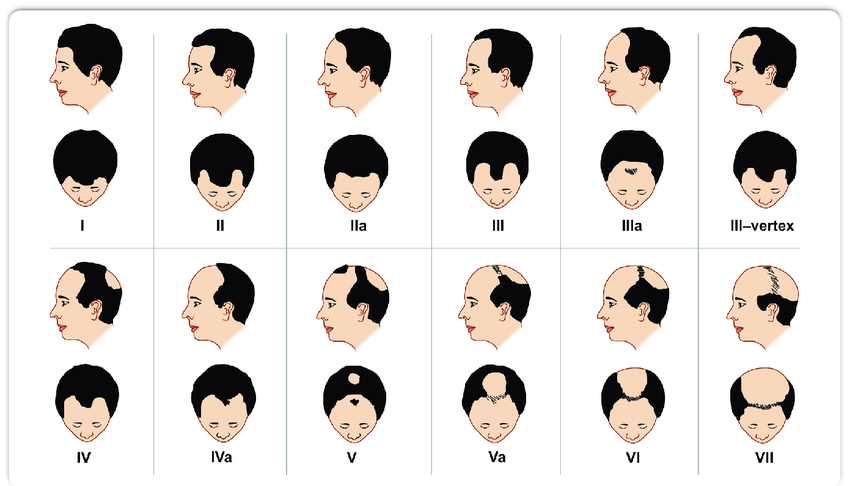
- **Androgenetic Alopecia in men** follows a predictable pattern of hair loss, starting with **bitemporal recession**, followed by **vertex thinning**, and eventually leading to **complete baldness**.
- SMP is an **effective solution for all Norwood stages**:
- **Norwood I-II**: Can be used for minor density enhancement.
- **Norwood III-V**: Creates a **shaved head illusion** or **enhances density in thinning areas**.
- **Norwood VI-VII**: Best suited for a **full scalp SMP treatment** to replicate the look of a shaved head.
- **Why SMP?**
- Suitable for patients who prefer a **shaved, buzzed look** without undergoing hair transplant surgery.
- Provides **a natural and consistent hairline reconstruction**.
- Ideal for those who **lack sufficient donor hair** for transplantation.
### **B. Female Pattern Hair Loss (FPHL) – Ludwig Scale**

- Female hair loss presents as **diffuse thinning**, usually **preserving the frontal hairline** while affecting the **mid-scalp and vertex**.
- SMP is an **excellent option for women** with:
- **Ludwig I-II**: Mild-to-moderate thinning.
- **Ludwig III**: More advanced thinning but still retaining some coverage.
- **Why SMP?**
- Creates the illusion of **fuller, denser hair** without requiring a shaved look.
- Works well for women who do **not want or are not candidates for a hair transplant**.
- Non-invasive and does not interfere with existing hair treatments.
---
## **1.3.2 Hair Transplant Scar Camouflage**
### **A. FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation) Scars**
- **FUT (strip method) hair transplants** leave a **linear scar** at the back of the head.
- SMP can **effectively camouflage** the scar by:
- Blending it into the surrounding hair follicles.
- Reducing its visual contrast against the scalp.
### **B. FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) Scars**
- **FUE procedures** create **hundreds to thousands of small dot-like scars**.
- SMP can be used to **conceal these small scars** by replicating the **appearance of natural follicles**.
### **C. SMP as an Enhancement for Hair Transplants**
- Some patients undergo **SMP after a transplant** to increase the **appearance of density** in areas where grafts may be sparse.
- SMP is useful in cases where **hair transplant results appear thin due to limited donor supply**.
---
## **1.3.3 Alopecia Conditions**
### **A. Alopecia Areata**
- **Alopecia Areata (AA)** is an **autoimmune condition** that causes **patchy hair loss**.
- SMP can:
- **Conceal localized bald spots** for patients with mild to moderate Alopecia Areata.
- **Even out the appearance of the scalp**, providing a more uniform look.
- **Reduce the contrast** between hair and bare patches.
### **B. Alopecia Totalis and Alopecia Universalis**
- **Alopecia Totalis** = Complete scalp hair loss.
- **Alopecia Universalis** = Complete body hair loss.
- In these severe cases, **SMP provides a full scalp micropigmentation solution**, creating a **shaved look that mimics a naturally buzzed head**.
---
## **1.3.4 Scarring and Trauma-Related Hair Loss**
### **A. Post-Surgical Scalp Scars**
- Patients who have undergone **head surgeries** (e.g., craniotomy) often develop visible **scalp scars**.
- SMP can **blend these scars** into the surrounding scalp by mimicking natural follicle patterns.
### **B. Trauma and Burn Scars**
- Accidents, injuries, and burns can leave **irregular, patchy areas of scarring** where hair no longer grows.
- SMP offers a **cosmetic camouflage solution**, making scars **less noticeable** by filling in affected areas with pigment.
---
## **1.3.5 Hair Density Enhancement for Thinning Hair**
### **A. SMP for Patients Who Do Not Want to Shave Their Head**
- Many individuals experience **diffuse thinning** but do not want to shave their hair completely.
- SMP can be applied **between existing hairs** to **reduce the contrast between hair and scalp**, making the hair **look fuller**.
### **B. SMP for Thin or Weak Donor Areas**
- Patients with weak donor areas may not have enough grafts for a **dense hair transplant**.
- SMP can **augment transplant results** by adding a **layered visual effect** of thicker hair.
---
## **1.3.6 Chemotherapy-Induced Hair Loss**
### **A. Cancer Patients and Scalp Micropigmentation**
- Chemotherapy can cause **temporary or permanent hair loss**.
- SMP offers an option for **cancer survivors** who want to **restore the appearance of hair**.
- Patients can choose:
- **A full shaved look SMP**.
- **Density enhancement SMP** if they retain some hair.
---
## **1.3.7 Non-Medical and Aesthetic Applications**
### **A. Hairline Restoration for Cosmetic Purposes**
- Some clients **do not have significant hair loss** but desire a **stronger, sharper hairline**.
- SMP is used for:
- **Lowering the hairline slightly**.
- **Creating a more defined, masculine appearance**.
- **Enhancing the natural density of an existing hairline**.
### **B. Beard and Eyebrow Micropigmentation**
- Some practitioners extend **micropigmentation techniques** to beards or eyebrows.
- SMP can create a **denser look in patchy facial hair**.
---
## **1.3.8 SMP for Different Skin Types and Ethnicities**
- **Scalp micropigmentation must be customized** based on **skin type, scalp color, and ethnicity**.
- **Lighter skin tones** require **lighter pigment shades**.
- **Darker skin tones** need **softer pigment application to avoid unnatural results**.
- Practitioners must account for **skin oiliness, pigment retention, and scar formation tendencies**.
---
## **1.3.9 Contraindications and When SMP Is Not Recommended**
### **A. Absolute Contraindications**
- **Active scalp infections** (e.g., folliculitis, ringworm).
- **Keloid-prone skin** (risk of hypertrophic scar formation).
- **Severe psoriasis or eczema on the scalp** (pigment retention issues).
- **Uncontrolled diabetes or poor wound healing**.
- **Allergy to tattoo pigments**.
### **B. Relative Contraindications**
- **Active hair restoration treatments** (e.g., patients using Minoxidil may need to pause before treatment).
- **Recent sunburn or scalp trauma**.
- **Ongoing chemotherapy (wait until completion and stabilization).**
---
# **Conclusion**
Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP) is a **versatile and effective cosmetic procedure** for individuals experiencing hair loss, scalp scarring, or thinning hair.
- It is used for **male and female pattern baldness**, **alopecia conditions**, **scarring**, **post-hair transplant enhancements**, and **chemotherapy-related hair loss**.
- SMP provides **a realistic, non-invasive alternative to surgical hair restoration**.
- Customization based on **individual hair loss patterns, skin tone, and ethnicity** is critical for achieving **optimal, natural-looking results**.
- While SMP is generally safe, **proper patient selection** and **awareness of contraindications** are necessary to **ensure successful outcomes**.