### Date : 2025-02-24 20:29
### Topic : Androgenetic Alopecia (AGA) #dermatology #SMP #hairtransplantation #alopecia
----
# **Androgenetic Alopecia (AGA)**
Androgenetic Alopecia (AGA) is the most **common cause of hair loss** in both men and women, often referred to as **male-pattern baldness (MPB) or female-pattern hair loss (FPHL)**. It is a **progressive, hereditary condition** driven by genetic and hormonal factors, primarily involving **androgens (male hormones), especially dihydrotestosterone (DHT)**.
---
## **1. What is Androgenetic Alopecia (AGA)?**
### **1.1 Definition**
- **Androgenetic Alopecia (AGA)** is a **genetic and hormonally influenced** condition that leads to **gradual, patterned hair loss** on the scalp.
- It is caused by the **miniaturization of hair follicles** due to the effects of **dihydrotestosterone (DHT)**.
- AGA is **not a disease** but rather a **physiological response to genetic sensitivity to DHT**.
### **1.2 Epidemiology**
- **Men**: 50% affected by age 50, 80% by age 70.
- **Women**: 30% affected by age 50, with an increasing prevalence post-menopause.
- More common in **Caucasians**, followed by Asians and Africans.
- Can start as early as **late teens to early 20s** in genetically predisposed individuals.
---
## **2. Causes and Pathophysiology of Androgenetic Alopecia**
### **2.1 Genetic Factors**
- AGA has a **strong genetic component**, inherited from **either the maternal or paternal side**.
- **Polygenic inheritance**: Multiple genes contribute to AGA susceptibility.
- **AR gene (Androgen Receptor gene)** on **chromosome X** plays a key role in AGA development.
### **2.2 Role of Androgens (DHT)**
- **Testosterone** is converted into **Dihydrotestosterone (DHT)** by the enzyme **5α-reductase (Type II and Type I)**.
- **DHT binds to androgen receptors** in scalp hair follicles, triggering:
- **Follicular miniaturization**: Hair follicles shrink, leading to thinner, shorter hair.
- **Shortened anagen (growth) phase**: Hairs grow for a shorter time before falling out.
- **Increased telogen (resting) phase**: More hair enters the shedding phase.
- **DHT-sensitive follicles are mainly located in the frontal, temporal, and vertex (crown) scalp**.

- **Occipital hair follicles** are resistant to DHT, which is why hair transplants use donor hair from this region.
### **2.3 Miniaturization of Hair Follicles**
- Normal follicle cycle:
**Anagen (growth) → Catagen (transition) → Telogen (resting/shedding) → Return to Anagen.**
- In AGA:
- The **anagen phase shortens** (normally lasts 2-6 years, but in AGA, it can be reduced to months).
- The **telogen phase lengthens**, leading to increased **hair shedding**.
- The **hair follicle becomes progressively smaller**, producing **vellus-like (thin, soft, colorless) hair**.
- Eventually, the follicle becomes **dormant and stops producing hair**.
---
## **3. Clinical Features of Androgenetic Alopecia**
### **3.1 Male Pattern Hair Loss (MPHL)**
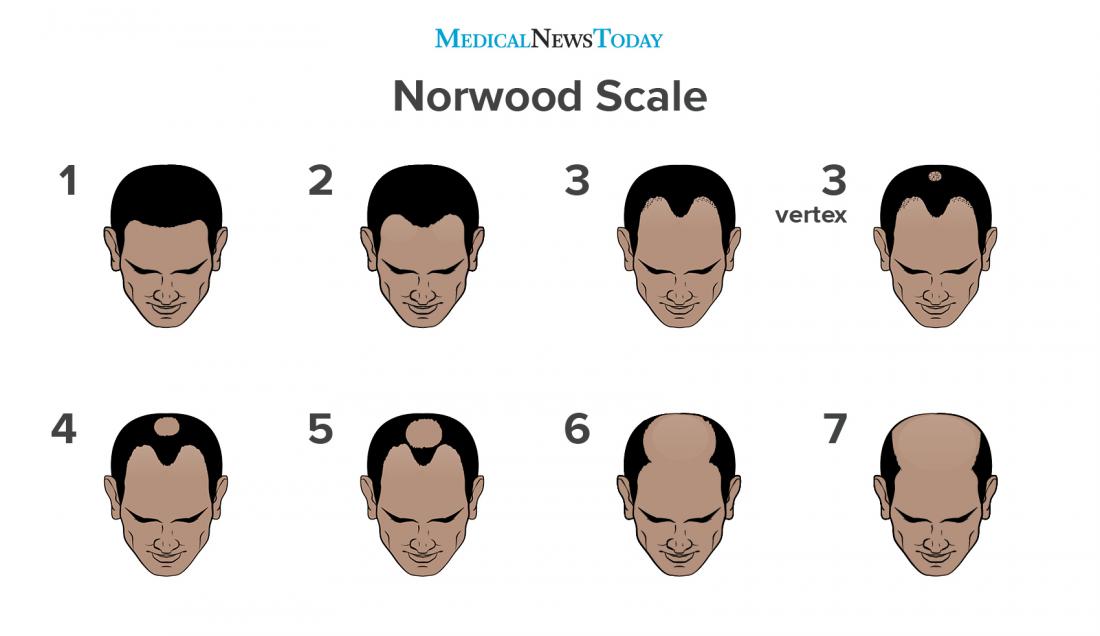
- Classified using the **Norwood-Hamilton Scale** (I-VII).
- Begins with **bitemporal recession** → **thinning at the vertex (crown)** → progresses to complete baldness.
- **Hairline recession** and **vertex thinning** are the hallmark signs.
### **3.2 Female Pattern Hair Loss (FPHL)**

- Classified using the **Ludwig Scale** (I-III).
- **Diffuse thinning at the central scalp**, **widening of the midline part**.
- Unlike men, **women usually retain their frontal hairline**.
### **3.3 Associated Features**
- **Scalp remains normal** (no redness, inflammation, or scaling).
- **Progression is slow** over several years to decades.
- **No hair loss in the occipital area** (back of the head).
---
## **4. Diagnosis of Androgenetic Alopecia**
### **4.1 Clinical Diagnosis**
- **History Taking**:
- Onset, duration, family history of AGA.
- Hair shedding pattern and presence of associated conditions (e.g., stress, hormonal imbalances).
- **Physical Examination**:
- Assess scalp hair thinning, miniaturization, and pattern of loss.
- Look for signs of **[[female hyperandrogenism]]** (e.g., acne, hirsutism in PCOS).
### **4.2 Trichoscopy (Dermatoscope Examination)**
- **Miniaturized hairs** (shorter, thinner, and variable in diameter).
- **Increased hair follicle empty spaces**.
- **Peripilar halo** (inflammatory pigmentation around follicles).
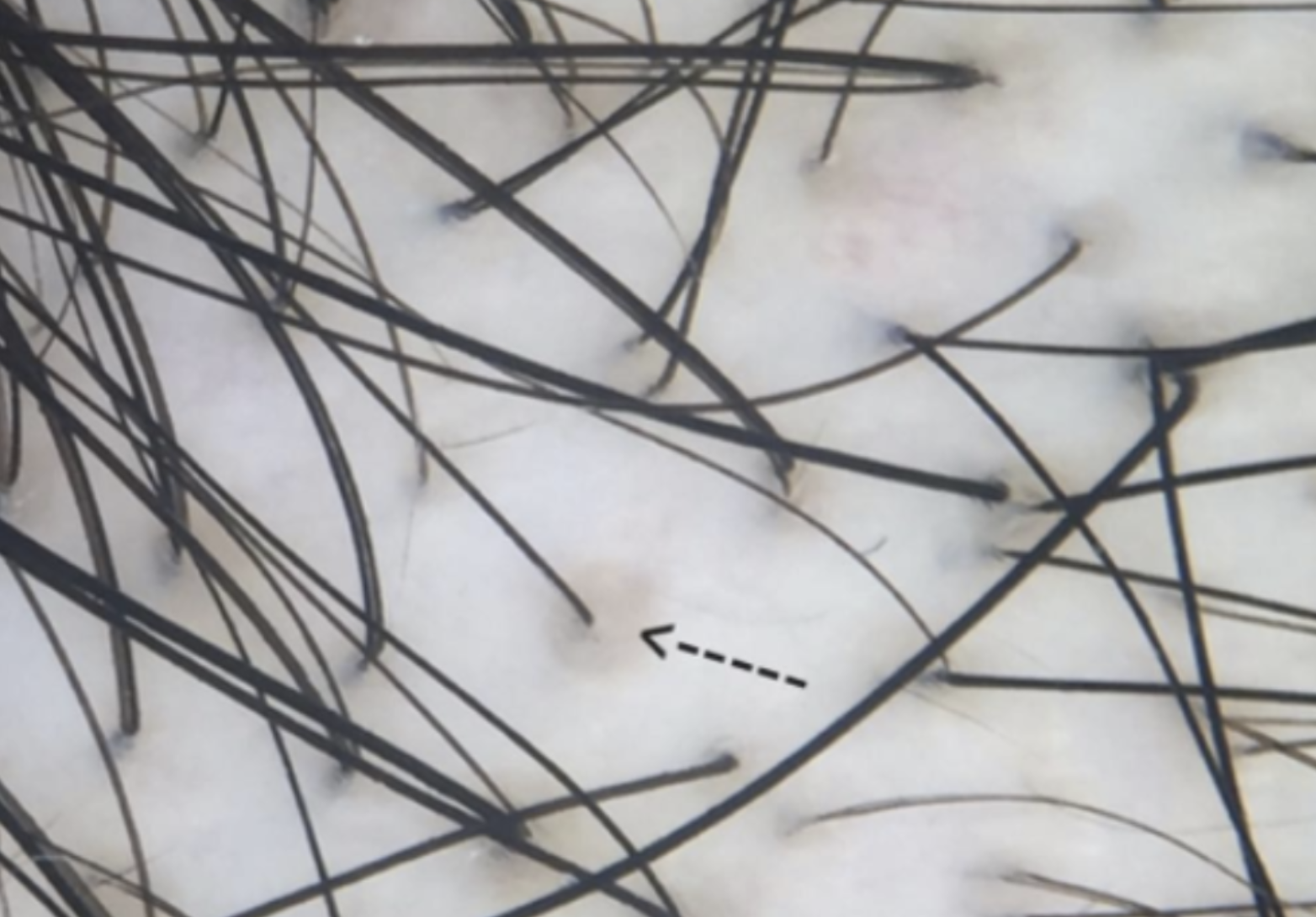

- **Variation in hair shaft diameter**.
### **4.3 Scalp Biopsy (If Needed)**
- Shows **increased vellus hair percentage**.
- **Perifollicular fibrosis** (chronic inflammation around hair follicles).
### **4.4 Laboratory Tests (If Female or Unusual Case)**
- **Hormonal Tests** (to rule out underlying endocrine disorders):
- **Testosterone, DHT, DHEA-S** (Androgens).
- **TSH, Free T4** (Thyroid function).
- **Ferritin** (Iron deficiency linked to hair loss).
---
## **5. Treatment Options for Androgenetic Alopecia**
### **5.1 Medical Treatments**
#### **1️⃣ Finasteride (5α-Reductase Inhibitor)**
- **Mechanism**: Blocks conversion of testosterone → DHT.
- **Effect**: Slows hair loss and promotes regrowth.
- **Dosage**: 1mg daily (oral).
- **Side Effects**: Erectile dysfunction, decreased libido, gynecomastia.
#### **2️⃣ Dutasteride (More Potent 5α-Reductase Inhibitor)**
- Blocks **both Type I and Type II 5α-reductase** (more effective than Finasteride).
- Used **off-label** for AGA.
- **Side effects similar to Finasteride but stronger**.
#### **3️⃣ Minoxidil (Topical Vasodilator)**
- **Mechanism**: Prolongs anagen phase, increases blood supply.
- **Dosage**:
- 5% solution (men), 2% solution (women).
- Applied **twice daily**.
- **Side Effects**: Scalp irritation, increased shedding initially.
#### **4️⃣ PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) Therapy**
- **Mechanism**: Growth factors stimulate hair follicles.
- **Efficacy**: Can be combined with Minoxidil/Finasteride.
---
### **5.2 Hair Transplant Surgery**
- **FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation)**: Strip harvesting from the occipital scalp.
- **FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction)**: Individual follicle grafts extracted.
- **DHT-resistant hair is transplanted** to balding areas.
---
### **5.3 Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP)**
- **Ideal for** patients who:
- Want the appearance of **a shaved scalp with uniform density**.
- Have **insufficient donor hair** for a hair transplant.
- Need to **camouflage transplant scars**.
- **Non-invasive alternative** that creates **the illusion of hair follicles**.
---
## **6. Prognosis and Prevention**
### **6.1 Prognosis**
- **Untreated AGA is progressive**.
- **Early treatment is crucial** to preserving hair.
### **6.2 Prevention**
- **Early use of Finasteride/Minoxidil**.
- **Avoid smoking and poor diet**.
- **Low-level laser therapy (LLLT)** may help stimulate follicles.
---
## **Conclusion**
Androgenetic Alopecia is a **genetically and hormonally driven** condition that leads to **progressive hair follicle miniaturization**.
📌 **Early diagnosis and intervention** are key to slowing progression.
📌 **Medical treatments (Finasteride, Minoxidil) are first-line options**.
📌 **Hair transplants and SMP are effective for advanced cases**.